Databases and Software
Databases & Software for Prediction of Sedimentary Architecture
We specialize in the development of databases and software for the prediction sedimentary architecture and heterogeneity, especially in subsurface reservoir successions:
- Fluvial Architecture Knowledge Transfer System (FAKTS);
- Shallow-Marine Architecture Knowledge Store (SMAKS);
- Database of Aeolian Sedimentary architecture (DASA);
- Point-Bar Stratigraphic Architecture Numerical Deduction (PB-SAND);
- DuneModeller;
- Deep-Marine Architecture Knowledge Store (DMAKS) is run by TRG, a closely allied research group.
New FAKTS, SMAKS, DASA and DMAKS analogue database interfaces
UNLIMITED ACCESS TO FRG-ERG-SMRG SPONSORS
https://clastics.shinyapps.io/fakts/
https://clastics.shinyapps.io/smaks/
https://clastics.shinyapps.io/dasa/
https://clastics.shinyapps.io/dmaks/ (TRG sponsors)
CURRENT SPONSORS LOGIN CREDENTIALS: Your company representative can provide a username and password to access these database applications. Alternatively, you can obtain login details from Luca Colombera or Nigel Mountney. Each sponsor company has a single set of login credentials, which are used by everyone in the company. Note that the login credentials to access these database applications are not the same as the person-specific login details used to access the main FRG-ERG-SMRG web site.Learn more and access the shinyFAKTS, shinySMAKS, shinyDASA and shinyDMAKS user guide here.
FAKTS - Fluvial Architecture Knowledge Transfer System
 The Fluvial Architecture Knowledge Transfer System (FAKTS) is a
relational database storing numerical and descriptive data about fluvial
sedimentary architecture coming from fieldwork and peer-reviewed literature, from both
modern rivers and ancient successions.
The Fluvial Architecture Knowledge Transfer System (FAKTS) is a
relational database storing numerical and descriptive data about fluvial
sedimentary architecture coming from fieldwork and peer-reviewed literature, from both
modern rivers and ancient successions.
The database encapsulates all the major features of fluvial sedimentary architecture (style of internal organization,
geometries, grain size, spatial distribution and reciprocal relationships of
genetic units) in a hierarchical fashion, classifying datasets either in
whole or in part according to both controlling factors (e.g. climate type,
tectonic setting), and context-descriptive characteristics (e.g. channel/river
pattern, dominant transport mechanism).
The FAKTS database stores aspects of fluvial sedimentary architecture that can be applied
to fluvial-reservoir characterization and prediction. The database serves as
a tool with which to achieve the following primary goals:
- generate quantitative facies models for bespoke classes of fluvial system;
- guide well correlation of fluvial sandstone bodies;
- condition object- and pixel-based stochastic reservoir models;
- predict the likely heterogeneity of geophysically imaged geobodies;
- inform interpretation of lithologies observed in core and predict 3D architecture;
- characterize subsurface reservoirs and aquifers to determine suitability for carbon capture and storage (CCS);
- characterize subsurface reservoirs and aquifers to determine geothermal potential;
- characterize subsurface reservoirs to determine potential for underground storage of hydrogen;
- characterize subsurface reservoirs to determine potential for underground storage of radioactive waste.
SMAKS - Shallow-Marine Architecture Knowledge Store
 The Shallow-Marine Architecture Knowledge Store (SMAKS) is a
relational database storing numerical and descriptive data about shallow-marine, paralic and lacustrine
sedimentary architecture coming from fieldwork and peer-reviewed literature, from both
modern systems and ancient successions.
The Shallow-Marine Architecture Knowledge Store (SMAKS) is a
relational database storing numerical and descriptive data about shallow-marine, paralic and lacustrine
sedimentary architecture coming from fieldwork and peer-reviewed literature, from both
modern systems and ancient successions.
The database
encapsulates all the major features of shallow-marirne, paralic and
lacustrine sedimentary architecture (style of internal organization,
geometries, grain size, spatial distribution and reciprocal
relationships of
genetic units) in a hierarchical fashion, classifying datasets
either in
whole or in part according to both controlling factors (e.g. climate
type,
tectonic setting), and context-descriptive characteristics (e.g.
river, wave, tide influence, shoreline setting, dominant transport
mechanism).
The SMAKS database stores aspects of shallow-marine, paralic and lacustrine sedimentary architecture that can be applied to reservoir characterization & prediction. The database serves as a tool with which to achieve the following primary goals:
- generate quantitative facies models for bespoke coastal & shallow-marine sedimentary systems that act as subsurface reservoir bodies;
- guide well correlation of shallow-marine sandstone bodies;
- condition object- and pixel-based stochastic reservoir models;
- predict the likely heterogeneity of geophysically imaged geobodies;
- inform interpretation of lithologies observed in core and predict 3D architecture;
- characterize subsurface reservoirs and aquifers to determine suitability for carbon capture and storage (CCS);
- characterize subsurface reservoirs and aquifers to determine geothermal potential;
- characterize subsurface reservoirs to determine potential for underground storage of hydrogen;
- characterize subsurface reservoirs to determine potential for underground storage of radioactive waste.
Download the SMAKS brochure
DASA - Database of Aeolian Sedimentary Architecture
 The Database of Aeolian Sedimentary Architecture (DASA) is a
relational database storing numerical and descriptive data about aeolian and related sedimentary architecture coming from fieldwork and peer-reviewed literature, from both
modern systems and ancient successions.
The Database of Aeolian Sedimentary Architecture (DASA) is a
relational database storing numerical and descriptive data about aeolian and related sedimentary architecture coming from fieldwork and peer-reviewed literature, from both
modern systems and ancient successions.
The database
encapsulates all the major features of aeolian sedimentary architecture (style of internal organization,
geometries, grain size, spatial distribution and reciprocal
relationships of
genetic units) in a hierarchical fashion, classifying datasets
either in
whole or in part according to both controlling factors (e.g. climate
type,
tectonic setting), and context-descriptive characteristics (e.g. bedform type, dune-field location, subenvironment setting).
DASA is the worlds largest & most sophisticated relational database specifically designed to characterize the geomorphology, sedimentology, stratigraphic architecture and regional stratigraphy of modern & ancient aeolian systems, and their preserved successions.
- develop quantitative facies models, specifically tailored for parameters describing particular spatio-temporal and environmental contexts;
- instruct & constrain forward stratigraphic models and 3D geocellular models for enhanced characterization of subsurface aeolian successions;
- empirical assessment of how aeolian systems respond to and how associated architectures record allogenic and autogenic processes that dictate stratigraphy;
- make quantitative predictions of lithological heterogeneities across multiple scales for subsurface aeolian geobodies that cannot be examined directly;
- generate informed interpretations of aeolian lithologies observed in core, for prediction of three-dimensional sedimentary architecture away from boreholes;
- characterize subsurface reservoirs and aquifers to determine suitability for carbon capture and storage (CCS);
- characterize subsurface reservoirs and aquifers to determine geothermal potential;
- characterize subsurface reservoirs to determine potential for underground storage of hydrogen;
- characterize subsurface reservoirs to determine potential for underground storage of radioactive waste.
Download the DASA brochure
PB-SAND - Point-Bar Stratigraphic Architecture Numerical Deduction
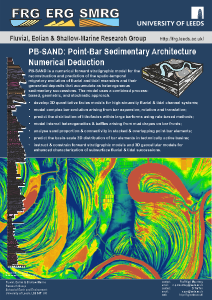 PB-SAND
is a numerical forward stratigraphic modelling software for the reconstruction and
prediction of the spatio-temporal migratory evolution of fluvial and
tidal meanders and their generated deposits that accumulate as
heterogeneous sedimentary successions. The model uses a combined
process-based, geometric, and stochastic approach. PB-SAND can be
applied for the following purposes:
PB-SAND
is a numerical forward stratigraphic modelling software for the reconstruction and
prediction of the spatio-temporal migratory evolution of fluvial and
tidal meanders and their generated deposits that accumulate as
heterogeneous sedimentary successions. The model uses a combined
process-based, geometric, and stochastic approach. PB-SAND can be
applied for the following purposes:
- Develop 3D and 4D quantitative facies models for high-sinuosity fluvial & tidal channel systems;
- Model complex bar evolution arising from bar expansion, rotation and translation;
- Predict the distribution of lithofacies within large barforms using rule-based methods;
- Model internal heterogeneities & baffles arising from mud drapes on bar fronts;
- Analyse sand proportion & connectivity in stacked & overlapping point-bar elements;
- Predict the basin-scale 3D distribution of bar elements in tectonically active basins;
- Instruct
& constrain forward stratigraphic models and 3D geocellular models
for enhanced characterization of subsurface fluvial & tidal
successions.
DuneModeller4D - Forward Stratigraphic Modelling Software
An overview of DuneModeller4D is coming soon.
DMAKS - Deep-Marine Architecture Knowledge Store

The Deep-Marine Architecture Knowledge Store is a relational database developed by the Turbidites Research Group (TRG) at the University of Leeds.
The DMAKS database stores numerical and descriptive data about
deep-marine systems and related sedimentary architecture coming from fieldwork and
peer-reviewed literature, from both
modern systems and ancient successions.
DMAKS is a quantitative database of the sedimentary architecture of deep-water depositional systems, which can be applied to problems of reservoir characterization and prediction. The database serves as a tool with which to achieve the following primary goals:
- Generate bespoke quantitative facies models for deep-marine and deep-lacustrine depositional systems, applicable as composite reservoir analogues;
- Guide well correlation of deep-marine sandstone bodies;
- Condition object- and pixel-based stochastic reservoir models;
- Predict the likely heterogeneity of geophysically imaged geobodies;
- Inform interpretation of lithologies observed in core, to guide conceptual models and predict 3D architecture.
Download the DMAKS brochure
Learn more about the Turbidites Ressearch Group Joint Industry Project (JIP) here.
FAKTS, SMAKS and DMAKS on Ava Clastics
To enhance sponsor impact, the FRG-ERG-SMRG has collaborated with
external partner PDS to develop a product that enables direct coupling
of the FAKTs, SMAKS and DMAKS databases with modelling workflows: Ava Clastics

 The Fluvial Architecture Knowledge Transfer System (FAKTS) is a
relational database storing numerical and descriptive data about fluvial
sedimentary architecture coming from fieldwork and peer-reviewed literature, from both
modern rivers and ancient successions.
The Fluvial Architecture Knowledge Transfer System (FAKTS) is a
relational database storing numerical and descriptive data about fluvial
sedimentary architecture coming from fieldwork and peer-reviewed literature, from both
modern rivers and ancient successions. The Shallow-Marine Architecture Knowledge Store (SMAKS) is a
relational database storing numerical and descriptive data about shallow-marine, paralic and lacustrine
sedimentary architecture coming from fieldwork and peer-reviewed literature, from both
modern systems and ancient successions.
The Shallow-Marine Architecture Knowledge Store (SMAKS) is a
relational database storing numerical and descriptive data about shallow-marine, paralic and lacustrine
sedimentary architecture coming from fieldwork and peer-reviewed literature, from both
modern systems and ancient successions. The Database of Aeolian Sedimentary Architecture (DASA) is a
relational database storing numerical and descriptive data about aeolian and related sedimentary architecture coming from fieldwork and peer-reviewed literature, from both
modern systems and ancient successions.
The Database of Aeolian Sedimentary Architecture (DASA) is a
relational database storing numerical and descriptive data about aeolian and related sedimentary architecture coming from fieldwork and peer-reviewed literature, from both
modern systems and ancient successions. PB-SAND
is a numerical forward stratigraphic modelling software for the reconstruction and
prediction of the spatio-temporal migratory evolution of fluvial and
tidal meanders and their generated deposits that accumulate as
heterogeneous sedimentary successions. The model uses a combined
process-based, geometric, and stochastic approach. PB-SAND can be
applied for the following purposes:
PB-SAND
is a numerical forward stratigraphic modelling software for the reconstruction and
prediction of the spatio-temporal migratory evolution of fluvial and
tidal meanders and their generated deposits that accumulate as
heterogeneous sedimentary successions. The model uses a combined
process-based, geometric, and stochastic approach. PB-SAND can be
applied for the following purposes: